Difference between revisions of "iMX8M Industrial EMC testing"
| Line 134: | Line 134: | ||
== Preparing the test == | == Preparing the test == | ||
=== Boot device and software === | === Boot device and software === | ||
| − | + | eMMC was selected as a booting device for all the boards. U-Boot settings were not adjusted as the default configuration was used. To prepare a fresh eMMC follow [[iMX6 TinyRex Max Creating Bootable microSD Card|these instructions]]. Here is an example of creating a eMMC suitable for Max configuration: | |
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
git clone https://github.com/voipac/imx6tinyrex_bin_linux | git clone https://github.com/voipac/imx6tinyrex_bin_linux | ||
Revision as of 08:48, 16 June 2022
Electromagnetic compatibility results for iMX8M Industrial Development Kit are shown on this page. Test setup and scripts are described in details.
These measurements were performed with boards using the actual hardware and software configuration of the web shop development kits.
Connected cables/devices
- Power source: +5V 40W power supply used for input voltage
- Storage device: eMMC Flash memory soldered on module used for booting, filesystem operation and script storage
- Ethernet: 1m long CAT Ethernet loopback cable connected. Forced to 100Mbps and used for ping test
- DisplayPort (M) interface used with LCD monitor connected: Full-HD output video stream generated and sent to LCD monitor via 2m long DisplayPort cable, with ferrite bead added. The output signal forced to be continuously generated, contributing to EMC spectrum, even though monitor was plugged into mains but not turned on, and laid flat on the floor to minimise its affect on results. Used LCD monitor: 29" LG UltraWide 29WP60G-B 2560x1080 px
- LCD Display: Newhaven LVDS Capacitive Display Set with 1024x600 resolution. LCD PN: NHD-10.1-1024600MB-LSXV-CTP
- 2x USB 3.0: SanDisk Ultra Flair 16GB USB 3.2 Gen 1, each connected through a 1m long USB 3.2 Gen 1 extension cable (Molex PN: 0687890035). Both used during read/write test
- USB-C: Kingston DataTraveler 80 32GB USB 3.2 Gen 1, connected through USB-C extension cable (Cable PN: FCR72003)
- Camera: Digilent MIPI-CSI Camera Set plugged to the baseboard, recognised by the kernel, not actively used during testing. Ferrite bead added close to the camera module (PN: SRP33.5x6.5x10)
- CAN: CANbus Module inserted, but not actively used. CAN cable not connected
- WiFi and Bluetooth: Soldered directly on COM, not actively used. Depending on the temperature range, the default SPB228-D-3 or alternative CM-276NF module populated. Two antennas plugged and connected
- Console cable: Micro USB extension cable used only to setup the development kit, not actively plugged in during the measurements
- SD card: SD card (Sandisk) plugged in but not actively used
- Microphone: Microphone connected but not actively used
- Headphones: Headphones connected but not actively used
- Speakers: Line Out connected but not actively used
Testing conditions and results
All the results were measured in compliance with the emission limits for FCC Class B (EMC standard EN 55032B). Class B devices are suitable for both residential and industrial applications as the norm standards use more restrictive limits.
iMX8M Industrial Development Kit Max - Module under heavy load – PASS
Test description:
- development kit configuration:
- iMX8M Industrial Module Max in Industrial temperature range
- iMX8M Development Baseboard in Extended temperature range
- CPU heavy testing threads using stressapptest
- DDR4 memory heavy testing threads using stressapptest
Radiated Emissions
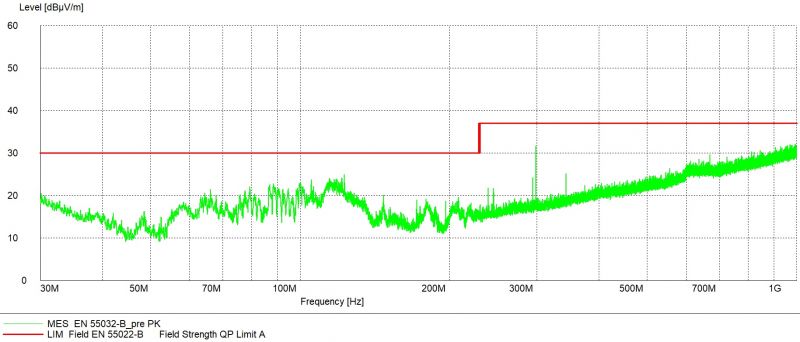
Both vertical and horizontal polarisation results in range from 30MHz to 1GHz were measured and captured during this EMC test session. Radiated emissions were measured and displayed as peak values. This relation is represented as a green curve in the measurements. The red highlighted line displays Class B limits. The Bilog antenna CBL6112A operating in range from 30MHz to 2GHz was used.
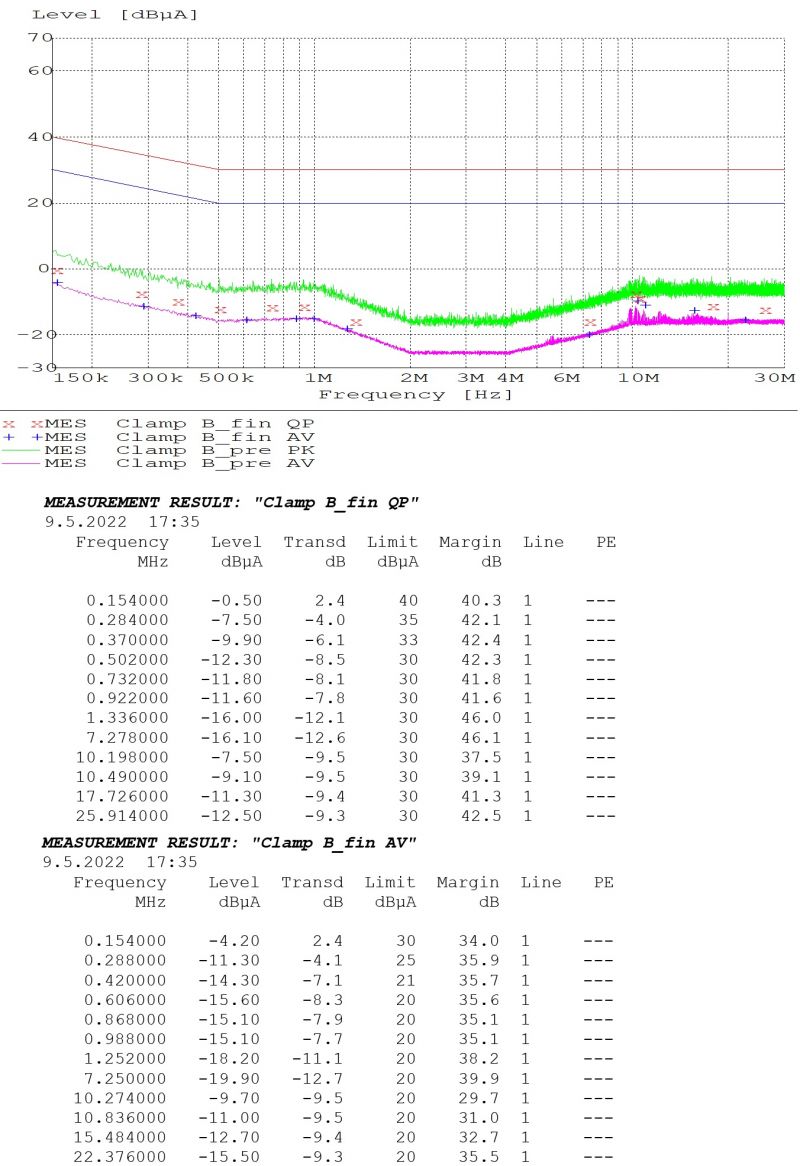
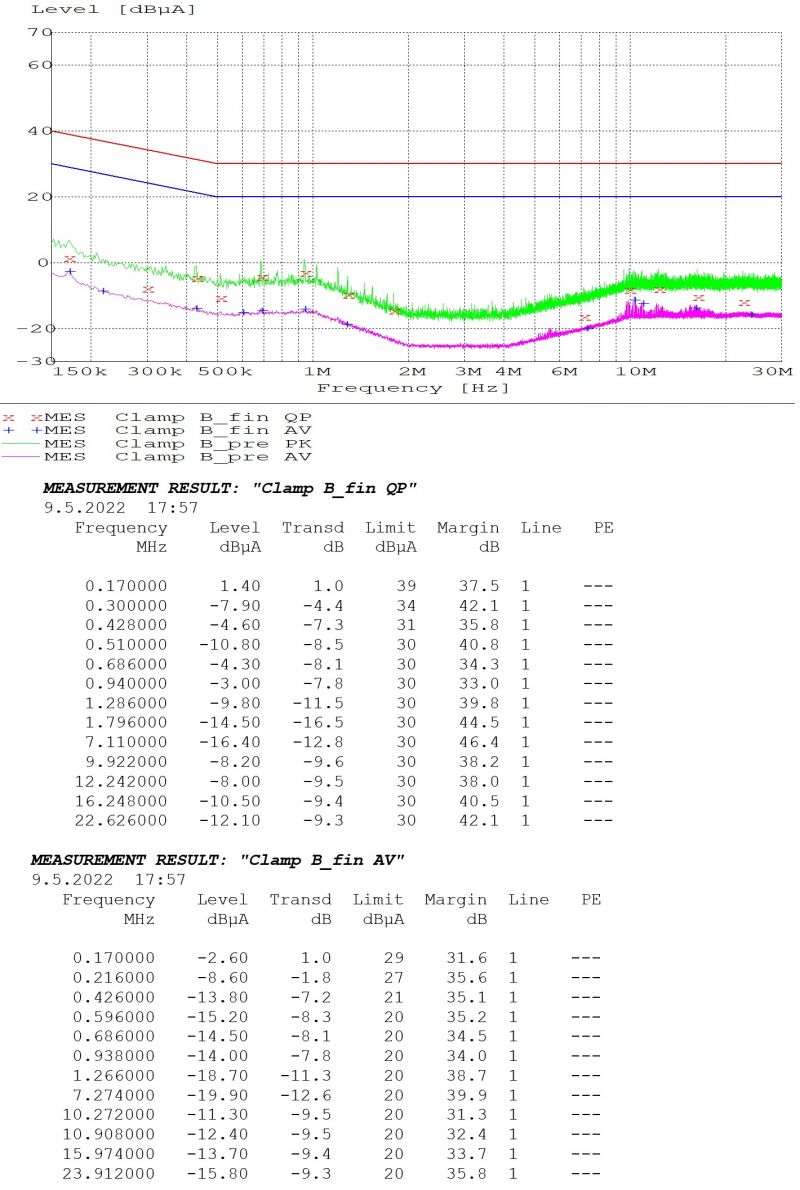
Conducted Emissions
iMX8M Industrial Development Kit Basic - Testing peripherals and external LCD display – PASS
Test description:
- development kit configuration:
- iMX8M Industrial Module Basic in Industrial temperature range
- iMX8M Development Baseboard in Extended temperature range
- CPU heavy testing threads using stressapptest
- DDR4 memory heavy testing threads using stressapptest
- Ethernet loopback cable used for network testing
- running heavy read/write testing for USB devices and SD card
- LCD Newhaven LVDS Capacitive Display Set actively used
- 2x USB 3.0 A read/write test
- USB-C
- Audio
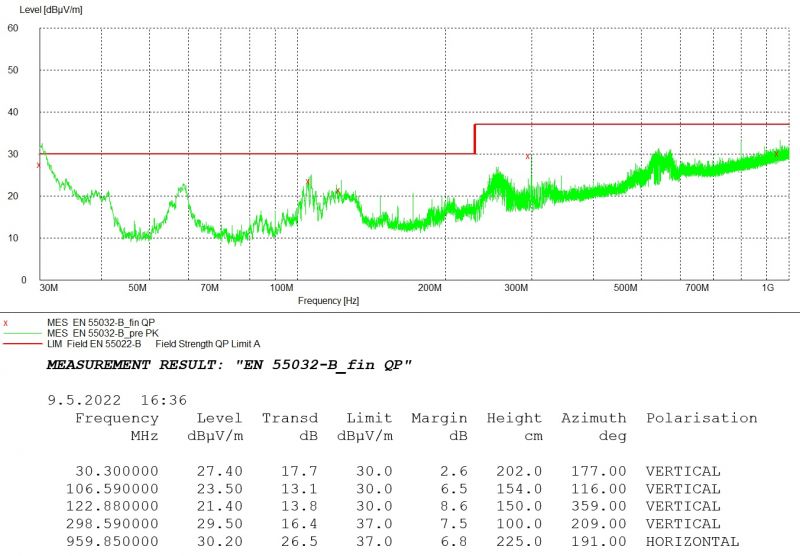
Radiated Emissions
The measurement starts with peak detection by scanning the whole frequency spectrum. This initial detection is plotted with the green curve MES_EN_55032-B_pre_PK. Afterwards the five highest peaks were pointed and measured more thoroughly by quasi-peak method. These real measured values of the radiation are displayed with the red crosses MES_EN_55032-B_fin_QP. The graph shows the setup passed the strict residential 55022-B limit represented by the red highlighted line.
These results prove that iMX8M Industrial Development Kit, even under heavy load, meets the stricter limits even if no enclosure is used.
Vertical + Horizontal polarisation in lower band 30MHz - 1GHz
Antenna used: Bilog CBL6112A 30 MHz to 2GHz
Vertical + Horizontal polarisation in higher band 1GHz - 6GHz
Antenna used: Double-Ridged Waveguide Horn Antenna 1GHz to 18GHz
File:iMX8M Industrial Basic-Radiated emissions 1-6GHz.png
Conducted Emissions
iMX8M Industrial Development Kit Max - Testing Ethernet and DisplayPort output - PASS
Test description:
- development kit configuration:
- iMX8M Industrial Module Max in Industrial temperature range
- iMX8M Development Baseboard in Extended temperature range
- CPU heavy testing threads using stressapptest
- DDR4 memory heavy testing threads using stressapptest
- Ethernet loopback cable used for network testing
- DisplayPort output tested in Full-HD 2560x1080 resolution
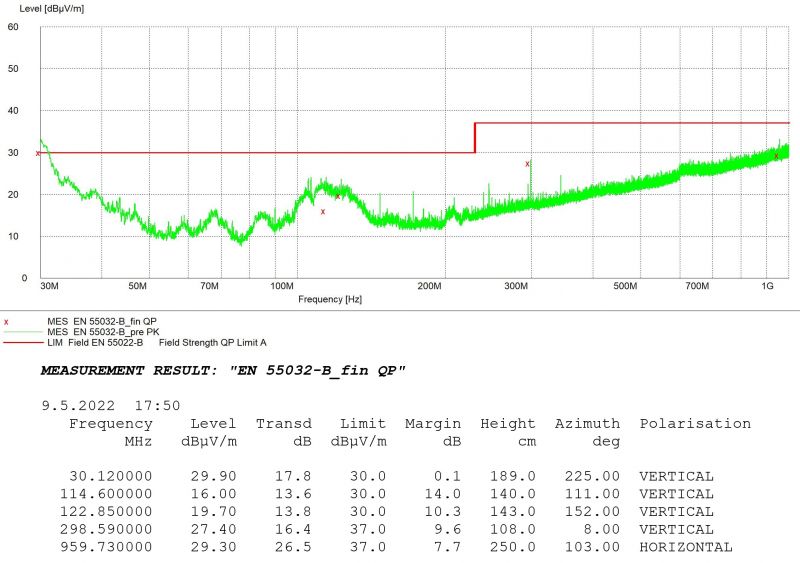
Radiated Emissions
The measurement starts with peak detection by scanning the whole frequency spectrum. This initial detection is plotted with the green curve MES_EN_55032-B_pre_PK. Afterwards the five highest peaks were pointed and measured more thoroughly by quasi-peak method. These real measured values of the radiation are displayed with the red crosses MES_EN_55032-B_fin_QP. The graph shows the setup passed the strict residential 55022-B limit represented by the red highlighted line.
These results prove that iMX8M Industrial Development Kit, even under heavy load, meets the stricter limits even if no enclosure is used.
Vertical + Horizontal polarisation in lower band 30MHz - 1GHz
Antenna used: Bilog CBL6112A 30 MHz to 2GHz
Vertical + Horizontal polarisation in higher band 1GHz - 6GHz
Antenna used: Double-Ridged Waveguide Horn Antenna 1GHz to 18GHz
File:iMX8M Industrial Max-Radiated emissions 1-6GHz.png
Running the script
Plug the board into mains and connect to it via console and copy code below
for a in $(seq 1 1 999) do for b in $(seq 1 1 999) do for c in $(seq 1 1 99) do for d in $(seq 1 1 99) do uptime echo "Test $a Test $b Test $c $d times" echo "Start stress-ng --iomix 1 -t 10 -v" stress-ng --iomix 1 -t 10 -v echo "End" echo "Start Thermal zone information" stress-ng --matrix 0 --tz -t 10 --log-brief -t 10 echo "End" ping -q -c1 192.168.0.2 >> env-chamber-testing.log if [ $? -ne 0 ] then echo "$(date +\%Y/\%m/\%d-\%T)($(date +\%Z)) ERROR: Ping failed" fi echo "End" done done done done
Preparing the test
Boot device and software
eMMC was selected as a booting device for all the boards. U-Boot settings were not adjusted as the default configuration was used. To prepare a fresh eMMC follow these instructions. Here is an example of creating a eMMC suitable for Max configuration:
git clone https://github.com/voipac/imx6tinyrex_bin_linux cd imx6tinyrex_bin_linux/ sudo ./fsl-sdcard-partition.sh -max /dev/mmcblk0
Starting DHCP server
The boards were mainly operated through SSH sessions. Thus it is very useful to have the same IP address during the whole process. The easiest way to do so is to run DHCP server on the controlling computer. To allow boards using the same address enable persistent leases with a long duration (2880 min used below):

Preserving SSH session
To minimise the possibility of results being affected, the control computer was disconnected and taken outside of the test chamber (after the board was setup).
When Ethernet cable connected to a board is disconnected, Linux terminates all the processes started within SSH sessions by default. Screen command allows to keep these sessions running. This command allow tasks to continue even if the cable is unplugged (and Ethernet loopback is plugged right away). It is important to make sure the filesystem includes this command:
sudo apt-get install screen
Running the script
Plug the board into mains and connect to it via SSH session. Screen environment is opened:
screen -S tinyrex
Testing scripts command consists of following arguments
- the first parameter - version of tested board (-max, -pro or -basic)
- the second parameter - USB drive 1 location
- the third parameter - USB drive 2 location
- the fourth parameter - SD card location
Several commands which were used during EMC testing are shown below:
- iMX8MQ Development Kit Pro:
./imx8mq-voipac-peripheral-test.sh -pro sda1 sdb1 mmcblk1p1 | tee -i imx8mq-emc-testing.log
- iMX8MQ Development Kit Max:
./imx8mq-voipac-peripheral-test.sh -max sda1 sdb1 mmcblk1p1 | tee -i imx8mq-emc-testing.log
- iMX8MQ Development Kit Basic:
./imx8mq-voipac-peripheral-test.sh -basic -n sda1 sdb1 mmcblk1p1 | tee -i imq8mq-emc-testing.log
Testing script
The complete script can be found in the downloads section.
#!/bin/sh
# iMX8MQ environmental chamber peripheral test
mountDevice() {
mkdir -p "/media/$2"
mount /dev/$1 /media/$2
cat /proc/mounts | grep -F "/dev/$1 /media/$2"
if [ "$?" -eq "0" ]; then
echo "$2 mounted"
else
echo "$2 not mounted"; exit 2
fi
}
# prepare files
cd ~/
mkdir -p env-chamber-testing/
cd env-chamber-testing/
touch env-chamber-testing.log
touch cpu-temp.log
basic=0
pro=0
max=0
case $1 in
-basic) basic=1 ;;
-pro) pro=1 ;;
-max) max=1 ;;
*)
esac
# mount devices
mountDevice $2 usb0
mountDevice $3 usb1
mountDevice $4 mmc0
updateLogFiles() {
# obtain board ID from IP address - be sure addresses are allocated based on MAC
boardID=$(/sbin/ip -o -4 addr list eth0 | awk '{print $4}' | cut -d/ -f1 | cut -d'.' -f4 | cut -d'2' -f2);
# be sure time server is running on DHCP server
currentTime=`date +%Y-%m-%d.%H:%M`
mv env-chamber-testing.log trx-board-$boardID-env-chamber.log.$currentTime
mv cpu-temp.log trx-board-$boardID-env-cpu-temp.log.$currentTime
}
finish_test_now() {
echo "$(date +\%Y/\%m/\%d-\%T)($(date +\%Z)) Ctrl+C Detected: End of the test"
precced=0;
#kill -INT $vid_pid $str_pid $log_pid;
sleep 3;
test_status=`cat env-chamber-testing.log | grep -i "error" | grep -v -e "0 errors" -e "no corrected errors"`
if [ -z "$test_status" ]
then
echo "*********TEST PASS*********"
else
echo "*********TEST FAIL*********"
echo "List of detected errors:"
cat env-chamber-testing.log | grep -i "error" | grep -v -e "0 errors" -e "no corrected errors" -e "List of detected errors:"
fi
updateLogFiles
exit;
}
# kill all processes if Ctrl+C is detected
trap finish_test_now 2
# play a video stream from HDMI input - testing also HDMI output
gst-launch-1.0 -q imxv4l2src ! autovideosink &
# stressapptest - one thread CPU, one thread memory, sata thread (if possible)
if [ "${basic}" -eq "1" ]; then
stress-ng --cpu 2 --vm 4 &
str_pid=$!
fi
if [ "${pro}" -eq "1" ]; then
stress-ng --cpu 4 --vm 4 &
str_pid=$!
fi
if [ "${max}" -eq "1" ]; then
stress-ng --cpu 4 --vm 4 &
str_pid=$!
fi
echo "$(date +\%Y/\%m/\%d-\%T)($(date +\%Z)) Starting stressapptest with PID: " $str_pid
proceed=1
# create test files
file1_path=`mktemp`
file2_path=`mktemp`
file1=`basename $file1_path`
file2=`basename $file2_path`
dd if=/dev/urandom of=$file1_path bs=1024 count=10000
dd if=/dev/urandom of=$file2_path bs=1024 count=10000
cp1_from="/media/mmc0/"
cp1_to="/media/usb0/"
cp2_from="/media/usb0/"
cp2_to="/media/usb1/"
#copy files in case they are missing
cp $file1_path $cp1_from
cp $file1_path $cp1_to
cp $file2_path $cp2_from
cp $file2_path $cp2_to
while [ $proceed -eq 1 ]
do
ping -q -c1 192.168.0.2 >> env-chamber-testing.log
if [ $? -ne 0 ]
then
echo "$(date +\%Y/\%m/\%d-\%T)($(date +\%Z)) ERROR: Ping failed"
fi
cp1_done=`ps | grep $cp1_pid | grep cp`
if [ -z "$cp1_done" ]; then # copy finished
if cmp -s $cp1_from$file1 $cp1_to$file1; then
echo "$(date +\%Y/\%m/\%d-\%T)($(date +\%Z)) PASS: Copying file from $cp1_from to $cp1_to successful"
else
echo "$(date +\%Y/\%m/\%d-\%T)($(date +\%Z)) ERROR: Difference between files on $cp1_from and $cp1_to detected"
fi
cp1_temp=$cp1_from # swap destinations
cp1_from=$cp1_to
cp1_to=$cp1_temp
rm $cp1_to$file1 # remove destination file
cp $cp1_from$file1 $cp1_to$file1 &
cp1_pid=$!
echo "$(date +\%Y/\%m/\%d-\%T)($(date +\%Z)) Started copying file from $cp1_from to $cp1_to"
fi
cp2_done=`ps | grep $cp2_pid | grep cp`
if [ -z "$cp2_done" ]; then # copy finished
if cmp -s $cp2_from$file2 $cp2_to$file2; then
echo "$(date +\%Y/\%m/\%d-\%T)($(date +\%Z)) PASS: Copying file from $cp2_from to $cp2_to successful"
else
echo "$(date +\%Y/\%m/\%d-\%T)($(date +\%Z)) ERROR: Difference between files on $cp2_from and $cp2_to detected"
fi
cp2_temp=$cp2_from # swap destinations
cp2_from=$cp2_to
cp2_to=$cp2_temp
rm $cp2_to$file2 # remove destination file
cp $cp2_from$file2 $cp2_to$file2 &
cp2_pid=$!
echo "$(date +\%Y/\%m/\%d-\%T)($(date +\%Z)) Started copying file from $cp2_from to $cp2_to"
fi
done